
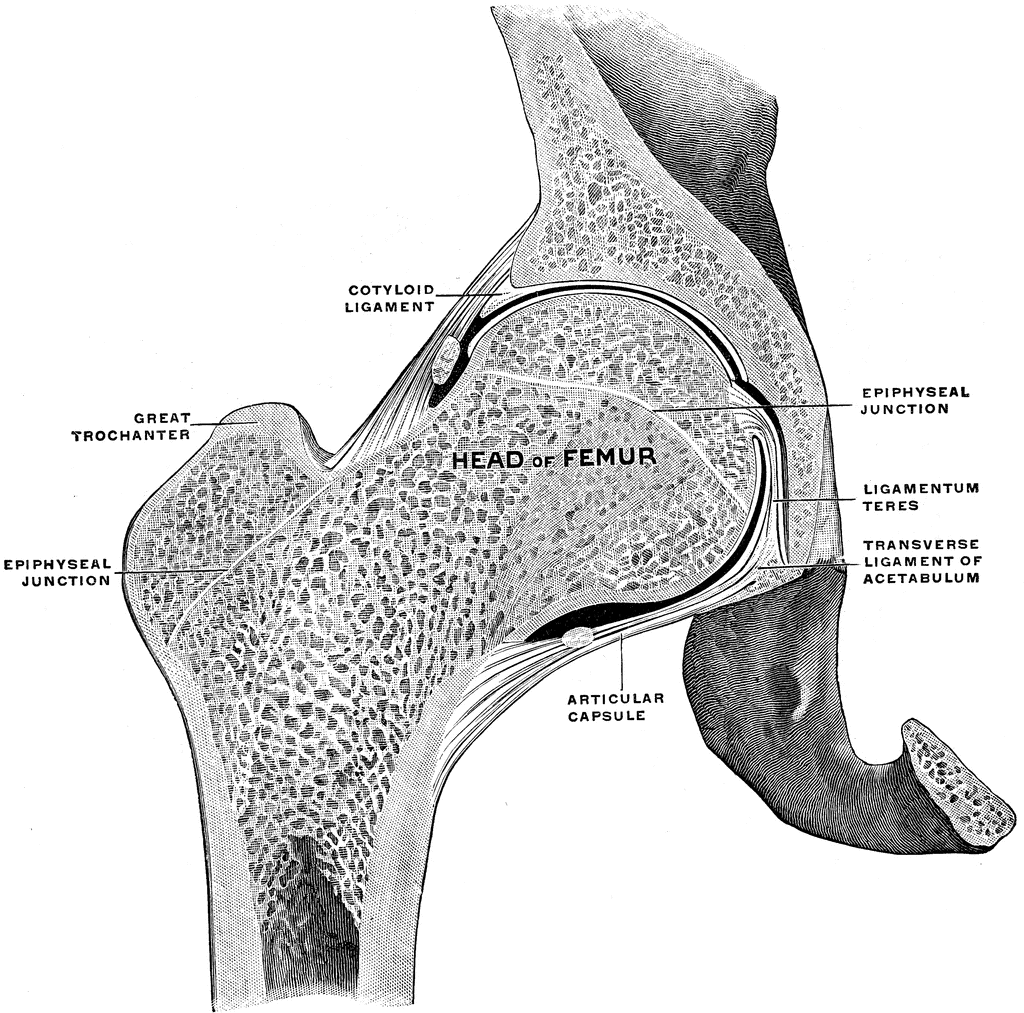
Nerves: Innervation is mainly provided by autonomic nerves and the pudendal nerve.Veins: follow the course of the arteries and are named accordingly.Arteries: mainly derived from the internal iliac artery.Perineum: superficial area between the anus and external genitalia.Anal triangle: consists of the anal canal, the external sphincter muscle, and the ischiorectal fossae.Urogenital triangle: consists of the perineal membrane and the deep and superficial perineal pouch.Perineal region: an anatomical region inferior to the pelvic floor.Layers of the pelvic floor: pelvic diaphragm, urogenital diaphragm, superficial perineal layer.Pelvic floor: complex fibromuscular structure that holds the pelvic organs in place separates the pelvic cavity superiorly from the perineal region inferiorly.Soft tissue structures: inner portion (lower uterine segment, cervix, vagina, vulva), outer portion ( pelvic floor).Pelvic planes: plane of the pelvic inlet, planes of the greatest and least pelvic dimension, plane of the anatomical outlet.Pelvic regions: pelvic inlet, pelvic cavity, pelvic outlet.Pelvic form: gynecoid, anthropoid, android, plateylpelloid.In both male and female individuals: pararectal fossa, ischiorectal fossa, retropubic space of Retzius.In male individuals: rectovesical pouch.In female individuals: rectouterine pouch, vesicouterine pouch.Pelvic spaces: anatomical spaces of the pelvic cavity.Bounded inferiorly by the pelvic floor, which holds the organs in place.Allows passage of gastrointestinal and urogenital structures into the pelvis, as well as arteries veins, muscles, and nerves.Pelvic cavity: the space within the pelvic girdle.The foramina of the pelvis (e.g., sciatic foramina, vascular and muscular lacuna) allow the passage of nerves, muscles, blood vessels, and lymphatics.A number of ligaments (e.g., iliolumbar ligament, sacroiliac ligament) stabilize and support the joints of the pelvis.Joints: lumbosacral joint, sacroiliac joint, sacrococcygeal joint, pubic symphysis, hip joint.The hip bones (os coxae): ilium, ischium, pubis.The shape of the pelvis differs significantly between male and female individuals.Largely immobile provides stability and supports proper transfer of weight from the vertebral column to the lower extremities, especially in the upright position.A ring-like structure of the axial skeleton that connects the vertebral column to the lower extremities (e.g., femur).Movements of the hip joint include flexion, extension, lateral and medial rotation, abduction, adduction, and circumflexion. The arterial supply of the femoral head is ensured by the foveolar artery and branches of the deep femoral artery. It connects the trunk to the lower extremities and supports dynamic and static body weight. The hip joint is located between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis on each side. The superficial gluteal muscles abduct and medially rotate the thigh, while the deep gluteal muscles are responsible for lateral rotation of the thigh. The gluteal region consists of the muscles that form the buttocks, which can be divided into a superficial and a deep muscle layer. Openings in the pelvic floor allow for the passage of the rectum, vagina, and urethra.

Located inferior to the pelvic cavity is the pelvic floor, a complex fibromuscular structure that prevents pelvic organ prolapse, helps maintain fecal and urinary continence, and separates the perineal region from the pelvic cavity. Anatomical spaces of the pelvic cavity (e.g., rectouterine pouch, rectovesical pouch) vary between male and female individuals because of their different reproductive organs. Located in the space within pelvic girdle is the pelvic cavity, which provides protection for abdominal and pelvic organs. The pelvic cavity is the space within the pelvic girdle it contains abdominal and pelvic organs, which are protected by the pelvic girdle. The pelvic girdle transmits body weight from the axial skeleton to the lower extremities and provides attachment to a large number of muscles and ligaments. In female individuals, the pelvis additionally accommodates the birth canal and therefore is larger and wider than in male individuals. Each hip bone consists of three fused bones: the ilium, ischium, and pubis. These bones are firmly connected by the pubic symphysis anteriorly and the sacrococcygeal and sacroiliac joints posteriorly. The bony pelvis ( pelvic girdle) is composed of the two hip bones, the sacrum, and the coccyx.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
